

MBBS (AIIMS), MS (Surgery, AIIMS), MNAMS, FACS (USA), FICS (USA), FUICC
Tue, 06 Feb 2024
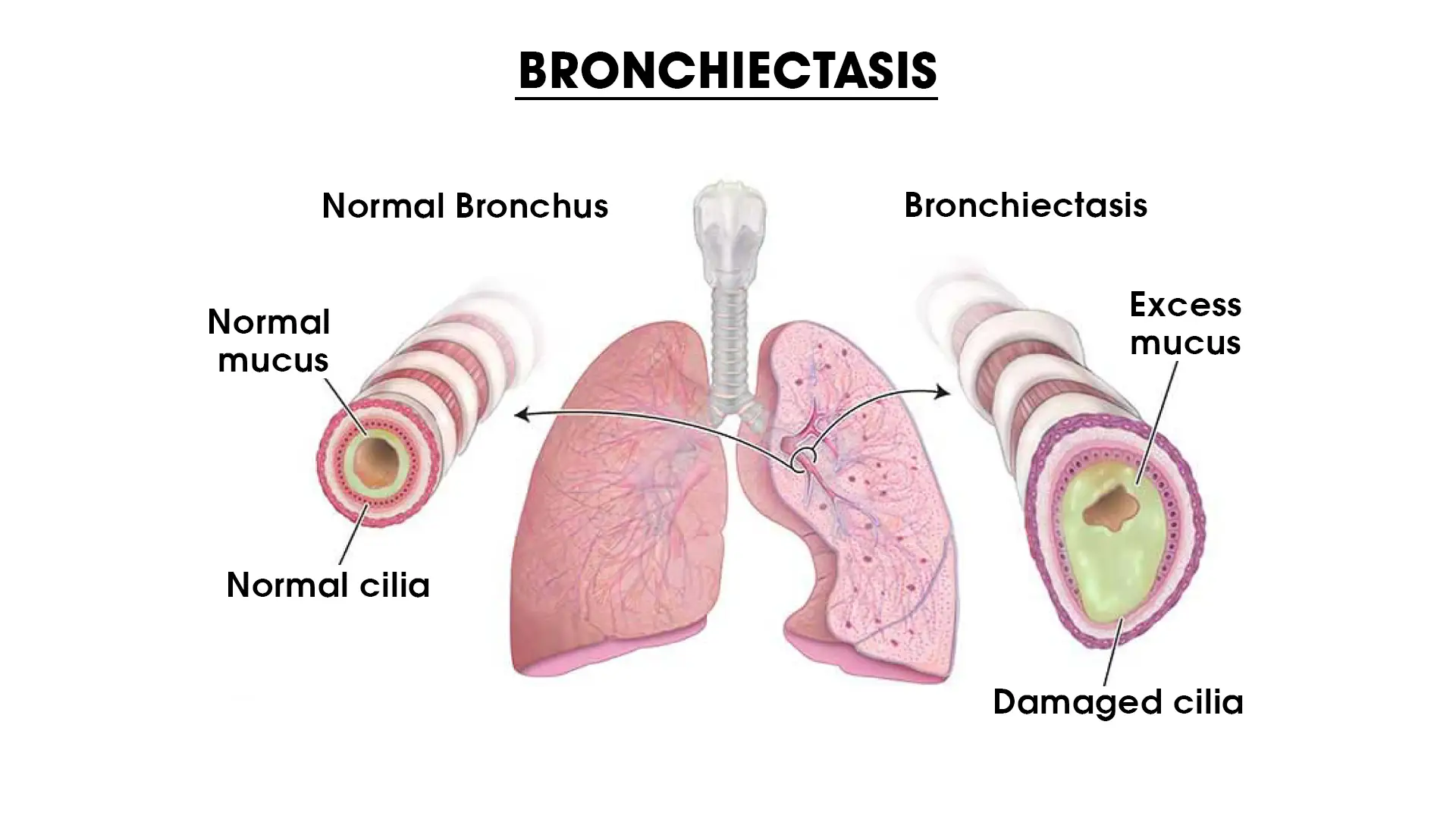
Among all the respiratory complications that Indians suffer from, around 5.9%–20.5% of the Indian population suffers from bronchiectasis, which is a chronic respiratory illness. The condition leads to the abnormal widening and thickening of the bronchial tubes present in the lungs.
Most patients diagnosed with bronchiectasis generally have a history of repeated lung infections, inflammation, or other underlying health issues that damage the airways.
Albeit its rarity, bronchiectasis can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. This is one of the reasons why being informed about the condition and its causes and symptoms is vital. We explain more about that in this guide.
Bronchiectasis is caused by an infection or other condition that injures the walls of the airways or prevents the airways from clearing mucus. Mucus helps remove inhaled dust, bacteria, and other small particles from the airways.
In bronchiectasis, your airways slowly lose their ability to clear out mucus. The mucus builds up and bacteria begin to grow. This leads to repeated, serious lung infections. To get the expert advice consult the best chest surgeon in India, Dr Arvind Kumar.
The onset of bronchiectasis can be due to congenital complications or acquired causes. Some of the most common causes include:
Bronchiectasis is caused by an infection or other condition that injures the walls of the airways or prevents the airways from clearing mucus. People with bronchiectasis may produce frequent green/yellow sputum, sometimes with blood also. However, it is possible to have "dry bronchiectasis" in which there is no sputum production. People with bronchiectasis may have bad breath indicative of active infection. Frequent bronchial infections and breathlessness are two possible indicators of bronchiectasis.
Bronchiectasis symptoms can vary from person to person, but common signs and symptoms include:
Although some of these symptoms are categorized as “common”, if these symptoms become recurrent and to a point that they affect one’s quality of life, it is vital to seek immediate medical advice before things take a turn for the worse.
In most cases, the diagnosis process starts with the patient presenting with the symptoms at the doctor’s clinic or hospital. If you are experiencing the above symptoms progressively worsening, scheduling an appointment is necessary.
During the consultation, diagnosis typically starts with a physical examination. Depending on the assessment, the specialist will then prescribe a few of the following diagnostic tests:
The results from these individual tests determine what the next steps would be in terms of treating the patient and their symptoms.
In most cases, Bronchiectasis can be treated non-surgically, especially if the condition is diagnosed earlier. However, you need to realize that this chronic disease doesn’t have a cure. Instead, the treatments generally involve symptom management to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Some of the treatment options include:
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition that can significantly impact a persons daily life. While it cannot be completely cured, it can be managed effectively with non-surgical and, in some cases if required surgical interventions.
If you are struggling with the condition or know someone who is, Dr. Arvind Kumar is a leading thoracic surgeon who can help you navigate through the situation with a personalized treatment plan addressing your specific needs. For more details, kindly contact us.
Copyright @ (Prof.) Dr. Arvind Kumar. All Rights Reserved / Thoracic Surgical Oncologis
License Number: U.P State Medical Council (India) No. 27637
