

MBBS (AIIMS), MS (Surgery, AIIMS), MNAMS, FACS (USA), FICS (USA), FUICC
Fri, 15 Dec 2023
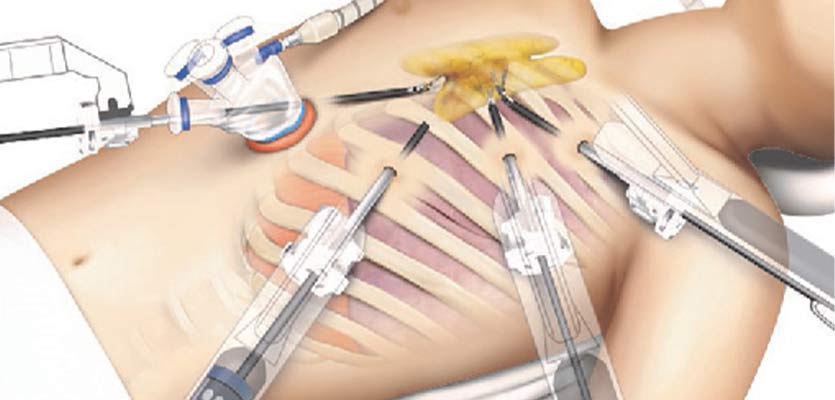
We have Indias largest experience in surgical removal of thymus gland (Thymectomy) using the state-of-art da Vinci Surgical Robot. This procedure requires only a few small incisions, which avoid a sternotomy (large incision that separates chest bone) and get back to your life earlier and with much better quality of life compared to open surgery.
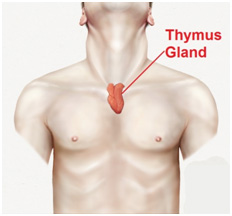
Thymus is a gland located in the middle of upper chest between the sternum (Breast Bone) and heart and possibly because of its central location in the upper chest between the lungs and next to the heart, ancient Greeks thought it might be the seat of the soul or the emotions.It wasnt until 1961 that medical science began to understand the actual functions of the thymus and its crucial relationship to the early development of the immune system.
In effect the thymus is the school for T-cells. T-cells (T-lymphocytes, where the T is for thymus) along with similar B-cells produced in bone marrow are a critical component of the bodys immune system. Each T-cell carries molecular receptors, something like locks for unique keys that match a specific foreign substance known as an antigen. If a T-cell lock meets its antigen key, it captures and kills it. This is how the body fights the invasion of antigens such as viruses, bacteria, certain poisons and anything else recognized by T-cells. The thymus is the organ that trains the T-cells to do this job.
However there are serious autoimmune diseases and cancers that affect the thymus and it is sometimes necessary to remove the organ in a procedure called a thymectomy. Fortunately, for all practical purposes removal of the thymus from an adult has minimal effect on the immune system.
The most common reasons for a thymectomy are related to:-
Approximately 10 to 15 percent of patients with Myasthenia Gravis will have a Thymoma. About 30% of those patients diagnosed with a Thymoma will have Myasthenia Gravis.
Thymoma is a type of cancer that begins in the thymus. Often, the distinction between a benign and a malignant thymoma is made during the actual surgery by assessing the degree to which the thymoma has invaded surrounding structures. Many patients with a thymoma are asymptomatic.
The treatment of thymoma with or without Myasthenia Gravis is complete removal of the thymus with the mass. Surgical approaches to removing a thymoma include a median sternotomy, clamshell incision and more recently Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS). The minimally invasive VATS procedure is reserved for early stage tumors. As experience with the daVinci robot is gained, a minimally invasive robotic approach to thymoma is considered appropriate for early stage lesions.
Should preoperative studies indicate that the lesion is invasive or malignant, surgeons will not attempt removal using minimally invasive techniques.
Early-stage thymoma cases are commonly treated with a thymectomy. Later stage thymomas and especially malignant thymoma are typically treated with chemotherapy or radiation, which may be followed by thymectomy.
However there are serious autoimmune diseases and cancers that affect the thymus and it is sometimes necessary to remove the organ in a procedure called a thymectomy. Fortunately, for all practical purposes removal of the thymus from an adult has minimal effect on the immune system.
The most common reasons for a thymectomy are related to:-
Approximately 10 to 15 percent of patients with Myasthenia Gravis will have a Thymoma. About 30% of those patients diagnosed with a Thymoma will have Myasthenia Gravis.
Thymoma is a type of cancer that begins in the thymus. Often, the distinction between a benign and a malignant thymoma is made during the actual surgery by assessing the degree to which the thymoma has invaded surrounding structures. Many patients with a thymoma are asymptomatic.
The treatment of thymoma with or without Myasthenia Gravis is complete removal of the thymus with the mass. Surgical approaches to removing a thymoma include a median sternotomy, clamshell incision and more recently Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS). The minimally invasive VATS procedure is reserved for early stage tumors. As experience with the daVinci robot is gained, a minimally invasive robotic approach to thymoma is considered appropriate for early stage lesions.
Should preoperative studies indicate that the lesion is invasive or malignant, surgeons will not attempt removal using minimally invasive techniques.
Early-stage thymoma cases are commonly treated with thymectomy. Later stage thymomas and especially malignant thymoma are typically treated with chemotherapy or radiation, which may be followed by thymectomy.
Surgical approaches
The Thymus gland is centrally located in the upper body and especially its nearness to the heart, the thymus presents specific challenges for surgery...Read More
Robotic Thymectomy
With the advent of robotic surgery, which is truly minimally invasive one can achieve the effectiveness of a transsternal approach without the...Read More
Advantages to patients
The patient undergoing a robotic-assisted thymectomy, the biggest advantages accrue from the minimally invasive approach and the precision of the internal surgical work...Read More
Q. How is robotic thymectomy different from traditional methods?
Robotic thymectomy utilizes minimally invasive robotic-assisted technology, offering smaller incisions, reduced scarring, and quicker healing compared to traditional open surgery. It is an advanced procedure with heightened precision and more accurate results, resulting in a quicker recovery period, further benefiting the patients.
Since the procedure utilizes advanced robotic instruments, it enables the surgeon to do the surgery through small incisions, which, in turn, contributes to reduced scarring, less postoperative pain, and a quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Q. What conditions can be treated with robotic thymectomy?
Some primary conditions targeted using robotic thymectomy include myasthenia gravis, thymomas, and other thymic disorders affecting the immune system.
In short, the treatment directly impacts and treats the conditions that are debilitating the functions of the thymus gland, impacting the immune system. Usually, a specialized approach is taken, and tailored treatment plans are implemented for satisfactory results.
Q. Who is a suitable candidate for robotic thymectomy?
If you have been diagnosed with myasthenia gravis, thymomas, or other thymic disorders and need to treat the conditions surgically, robotic thymectomy is often the treatment of choice. It is precise and targeted, and the effectiveness of the treatment further makes it an ideal route for treatment for the majority of the patients.
Our team will perform a comprehensive examination to evaluate the best route of treatment for you and analyze if you’d benefit from robotic thymectomy before proceeding with the said procedure.
Q. What are the potential benefits of choosing robotic thymectomy?
Robotic thymectomy offers many advantages such as reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and improved cosmetic outcomes. In most cases, patients and even surgeons prefer the robot-assisted surgical procedure because of the effectiveness and the desired results.
Besides the recovery and satisfactory results, one thing about this procedure that stands out is improved cosmetic results due to smaller incisions.
Q. What is the recovery process like after robotic thymectomy?
The recovery process after robotic thymectomy is characterized by its relatively swift and efficient nature, owing to the minimally invasive approach of the procedure. Patients typically experience less postoperative pain, reduced hospitalization time, and a quicker return to normal activities than traditional open surgery.
Once the surgery is over, the patients are transferred to the recovery room. The initial recovery period involves managing any immediate postoperative discomfort, which is often less pronounced than open surgery due to the smaller incisions. On average, patients are deemed fit to resume their normal activities after 2-4 weeks of the surgery.
Q. Are there risks associated with robotic thymectomy?
While considered safe, like any surgical procedure, robotic thymectomy carries potential risks such as infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
This is one of the primary reasons why our surgeons and specialists prioritize open communication with the patient before the surgery to give them a complete rundown of what to expect from the procedure and the treatment to ensure that the patients can make informed decisions.
Copyright @ (Prof.) Dr. Arvind Kumar. All Rights Reserved / Thoracic Surgical Oncologis
License Number: U.P State Medical Council (India) No. 27637
