

MBBS (AIIMS), MS (Surgery, AIIMS), MNAMS, FACS (USA), FICS (USA), FUICC
Mon, 22 Jan 2024
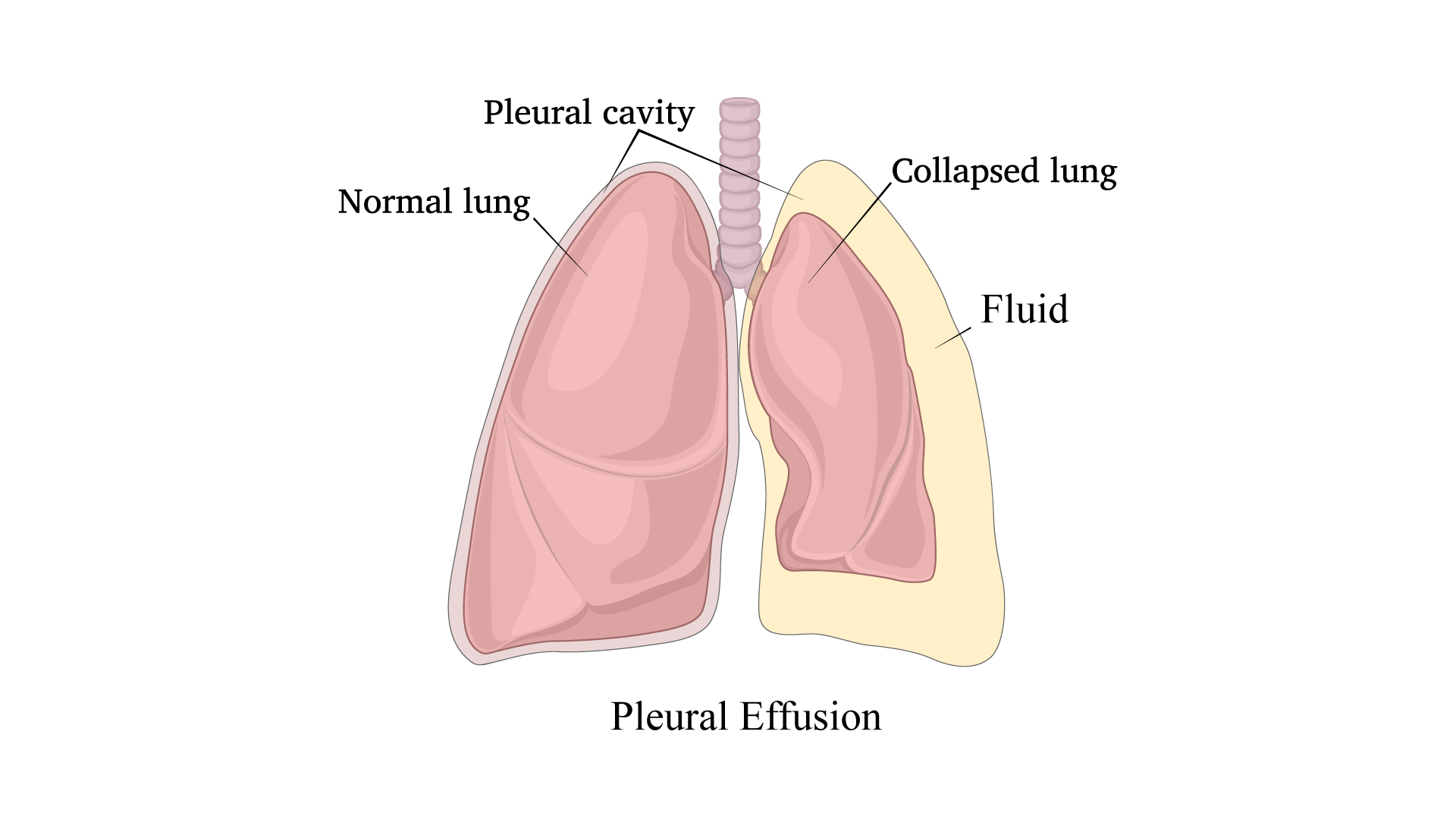
Respiratory health and function may be significantly impacted by pleural effusion, a disorder marked by the buildup of extra fluid in the pleural cavity. When the delicate equilibrium of the production of fluid and drainage inside the chest is compromised, this disease develops. It is essential for both patients and medical professionals to comprehend pleural effusion, its origins, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments. To get expert advice it is suggested to consult the best chest surgeon in India. Dr Arvind is one of the trusted and reliable surgeons in India.
Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. Excessive amounts of such fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during ventilation.
Pleural Effusion (Fluid in the Lungs) is a condition with an abnormal collection of fluid in the Chest Cavity. The pleura is a thin membrane that lines the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall outside the lungs. In pleural effusions, fluid accumulates in the space between the layers of pleura.
Read More :- Lung Transplant
Excessive fluid may accumulate because the body does not handle fluid properly (such as in heart failure, or kidney and liver disease). The fluid or water in pleural effusions also may result from inflammation, such as in Pneumonia, Tuberculosis and many other conditions. In our country, Pneumonia and Tuberculosis are two of the commonest causes of Pleural Effusion.
The most common symptom of pleural effusion is shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing. As the effusion grows larger the more difficult it is for the person to breathe. Chest pain is also a symptom of pleural effusion and occurs because the pleural lining of the lung is irritated. The pain is usually described as a sharp pain, worsening with a deep breath. The commonest cause of Pleural Effusion in our country is tuberculosis however, it can occur due to tumors (cancers) and numerous other causes also.
Note- In case of persistence symptoms consult your expert and get the expert advice.
The diagnosis is made by the analysis of the fluid aspirated from the chest. If inconclusive it can be repeated two or three times.
However, if the aspiration is inconclusive and fails to provide an answer, key-hole visualization of inside of the chest (diagnostic thoracoscopy) is the procedure of choice and provide the answer in almost all of the cases.
Read More:- Lung Cancer Program
The Treatment of pleural Effusion primarily depends on the cause: Aim of treating pleural effusion is to treat the cause effectively. Hence pleural effusion due to pneumonia is treated with antibiotics. Pleural Effusion due to tuberculosis is treated with Anti-tubercular Medicines.
When the amount of pleural fluid is large and causing breathlessness, drainage of the fluid (Thoracentesis) is done to improve breathing. If it recurs again & again, a chest tube (or a pig tail catheter) may be inserted. Sometimes, the fluid becomes "Pus" and form a layer around the collapsed lung of forms multiple septations in the pus.
This condition is now called "Empyema" (Pus around the Lungs) and need "Decortication" procedure. In this, we remove the thick layer (peel) from around the lung, thereby freeing it up to expand fully. Simultaneously, all the septations are broken, thorough wash is done to clear any infectious material and fresh chest tube is put under vision to drain any re-collection.
Traditionally, this procedure i.e. Decortication is done by Open method which involves cutting muscles & ribs resulting in weeks to months to recovery. We at Centre for Chest Surgery do the "SAME" procedure by Key-hole (VATS) Surgery where the whole procedure is carried out by 2-3 cm size holes, with no cutting of muscles or ribs. Patients have much "less pain" and blood loss and recover much faster, mostly back to work in few weeks, apart from cosmetically better outcome.
Sometimes the fluid accumulates due to involvement of pleura by cancer. In such cases, we drain the fluid by Chest tube to complete Lung expansion & put some chemicals (Pleurodesis) to fuse the pleural layers to prevent recurrence of pleural effusion.
In order to reduce symptoms, enhance lung function, and address the underlying cause of pleural effusion, fast and proper treatment is necessary. The etiology, the degree, and the patients general health prior to the existing condition, all play a role in the treatment.
Pleural effusion can be treated using a minimally invasive procedure called video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). Small incisions are made using this method, and tiny cameras and surgical instruments are introduced. Compared to open surgery, VATS has a number of benefits, including less discomfort, less time in the hospital, and quicker recovery.
Read More :- Dr. Arvind Kumar
Using VATS, the surgeon may see the pleural space clearly, find the source of the effusion, and carry out operations like drainage or pleurodesis. When treating recurring pleural effusion or if a certain diagnosis is required, this minimally invasive technique is very beneficial. An accurate, patient-friendly method of treating problems associated with pleural effusion is VATS surgery.
Pleural effusion must be thoroughly evaluated by a medical specialist in order to pinpoint the underlying reason and choose the best course of therapy. A patients entire health and quality of life can be considerably enhanced by prompt and effective therapy.
Copyright @ (Prof.) Dr. Arvind Kumar. All Rights Reserved / Thoracic Surgical Oncologis
License Number: U.P State Medical Council (India) No. 27637
